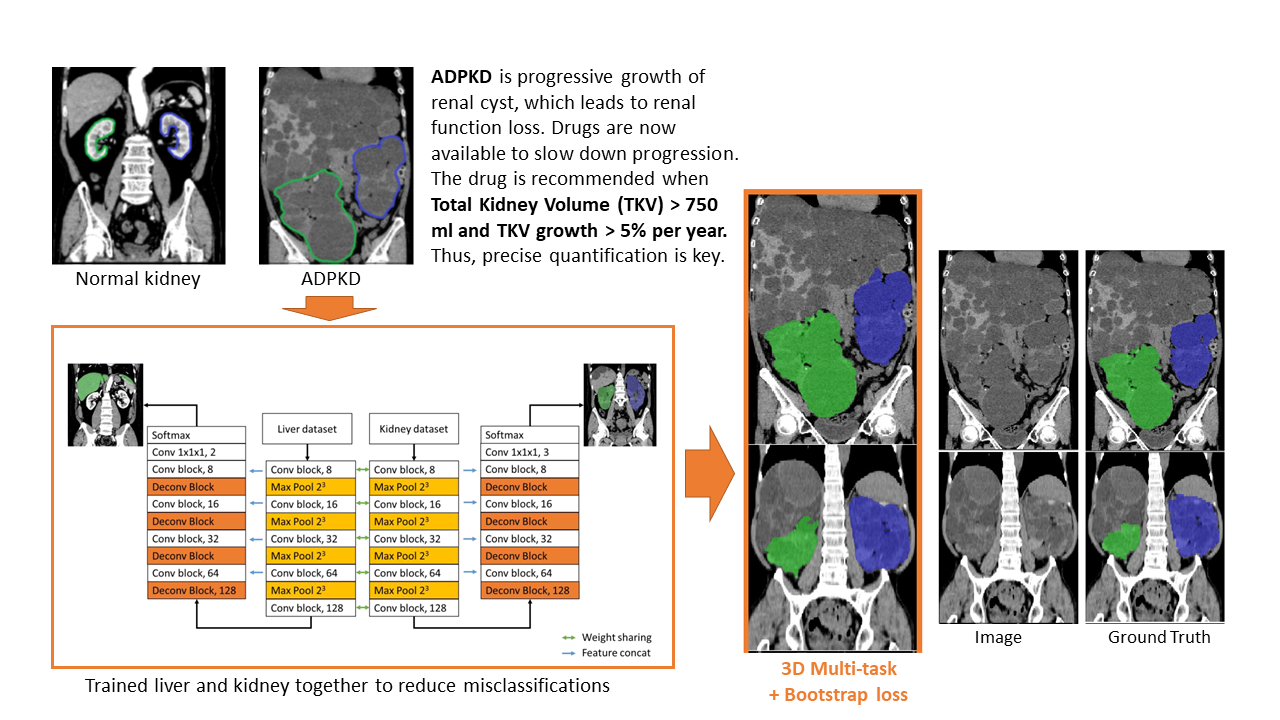
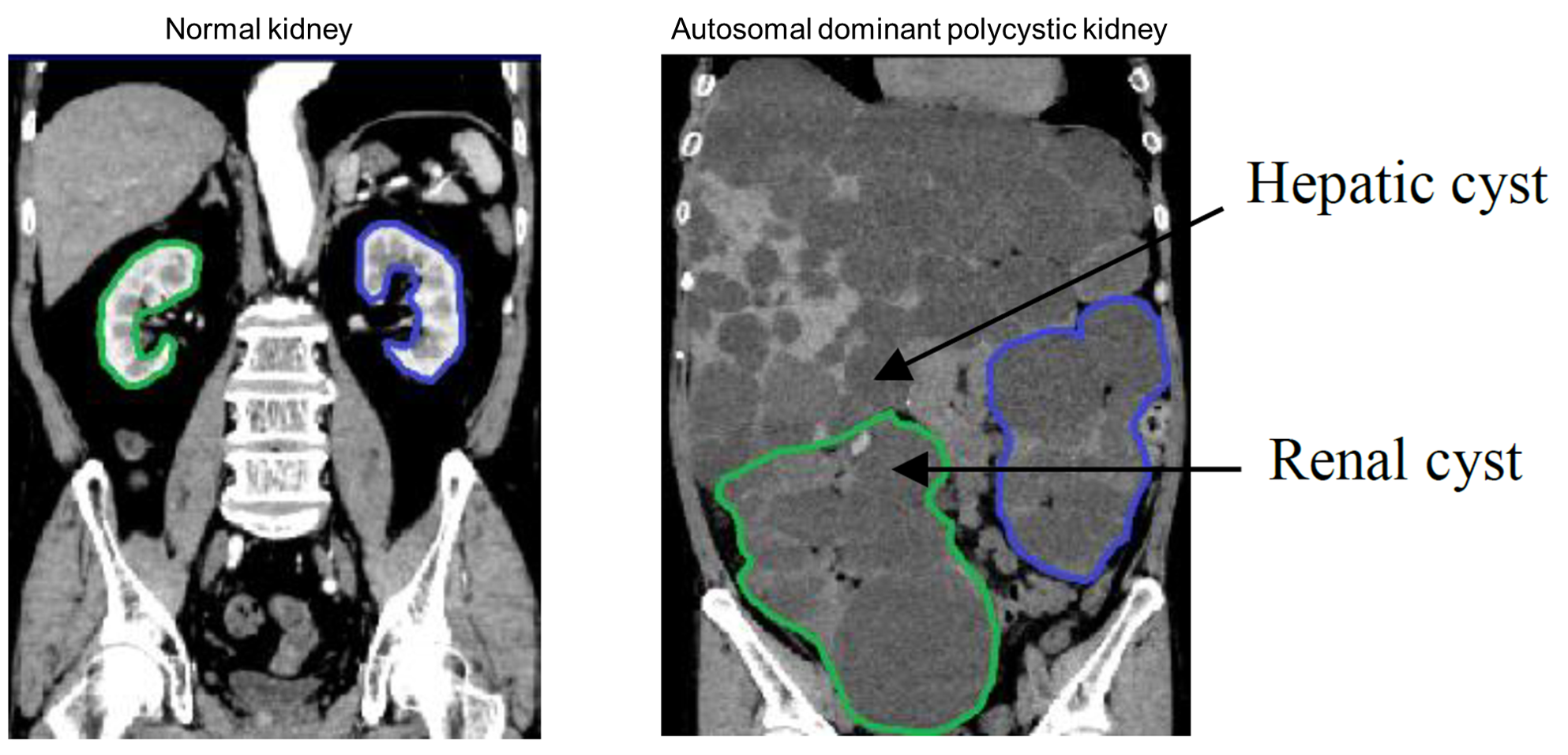
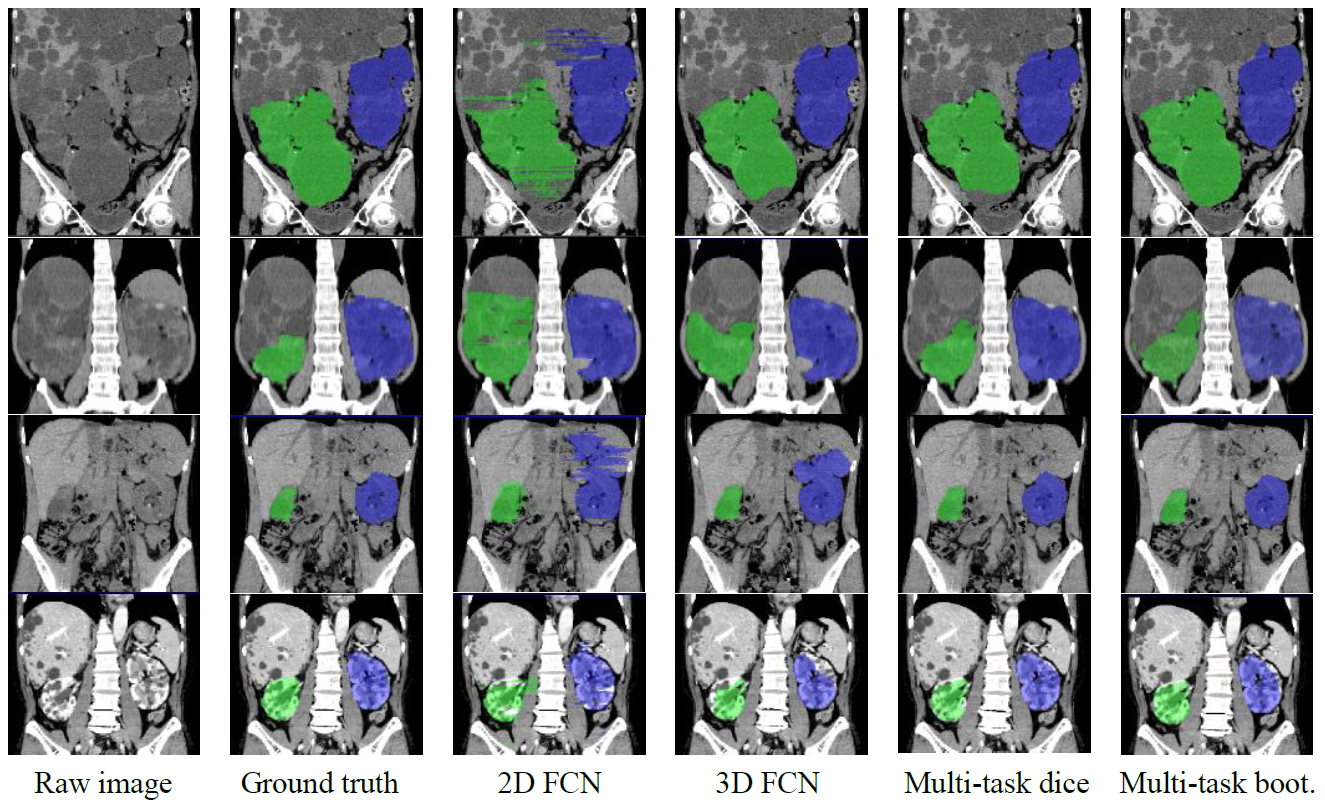
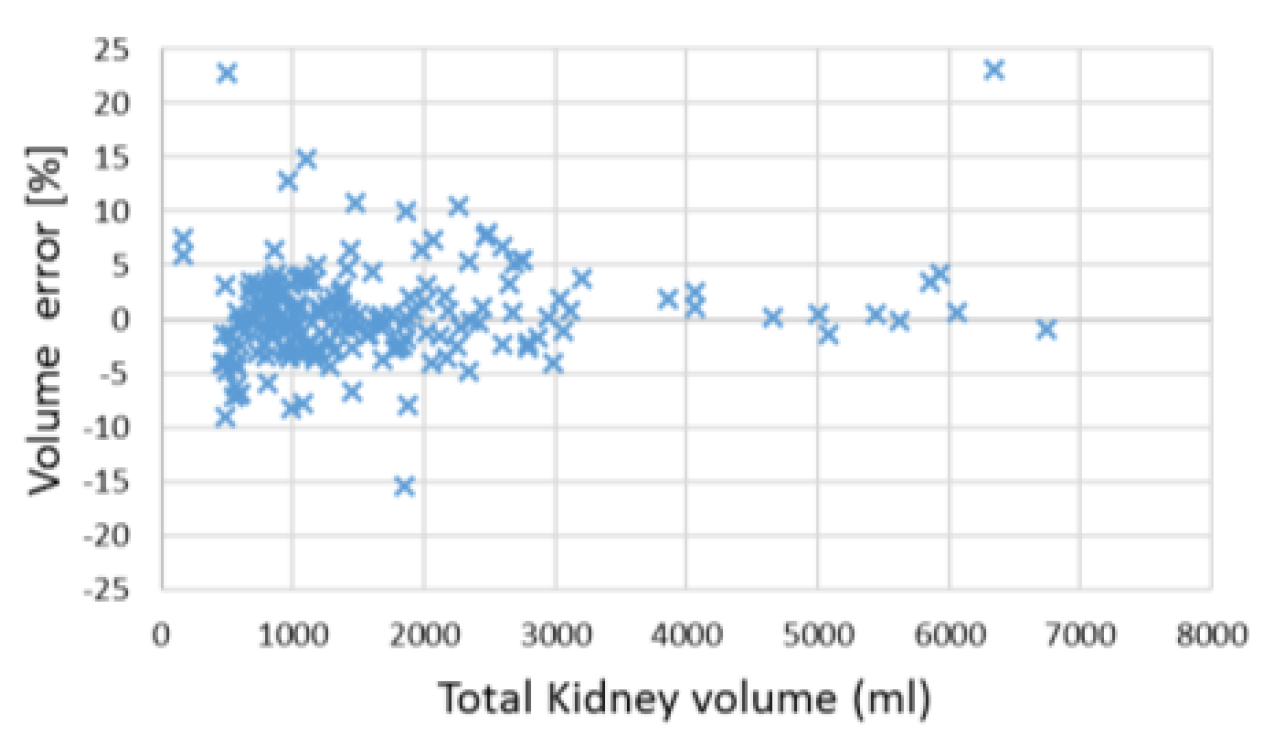
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is an inherited disease that causes numerous cysts (fluid-filled sacs) to develop in kidneys (Figure 1). With recent advances in medicines, drugs exist which can slow the rate of cysts growth. It is recommended that these drugs be used after evaluation of the patient’s age and stage of disease, as well as whether the disease is progressing rapidly. Rapid progression means total kidney volume (TKV) increases of over 5% per year. In other words, TKV should be measured within 5% precision to be useful in clinical practice. In this paper [1], authors propose multi-task 3D Convolutional Neural Networks to segment ADPK and simply bootstrap cross entropy loss. Experiments show that mean absolute percentage TKV error achieve 3.86% (Figure 2, 3). In the future, it is hoped that ADPK can be segmented with greater accuracy, which will help in the management and treatment of ADPK.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00919-9_44
CAUTION:This is Fujifilm Global Website. Fujifilm makes no representation that products on this website are commercially available in all countries. Approved uses of products vary by country and region. Specifications and appearance of products are subject to change without notice.