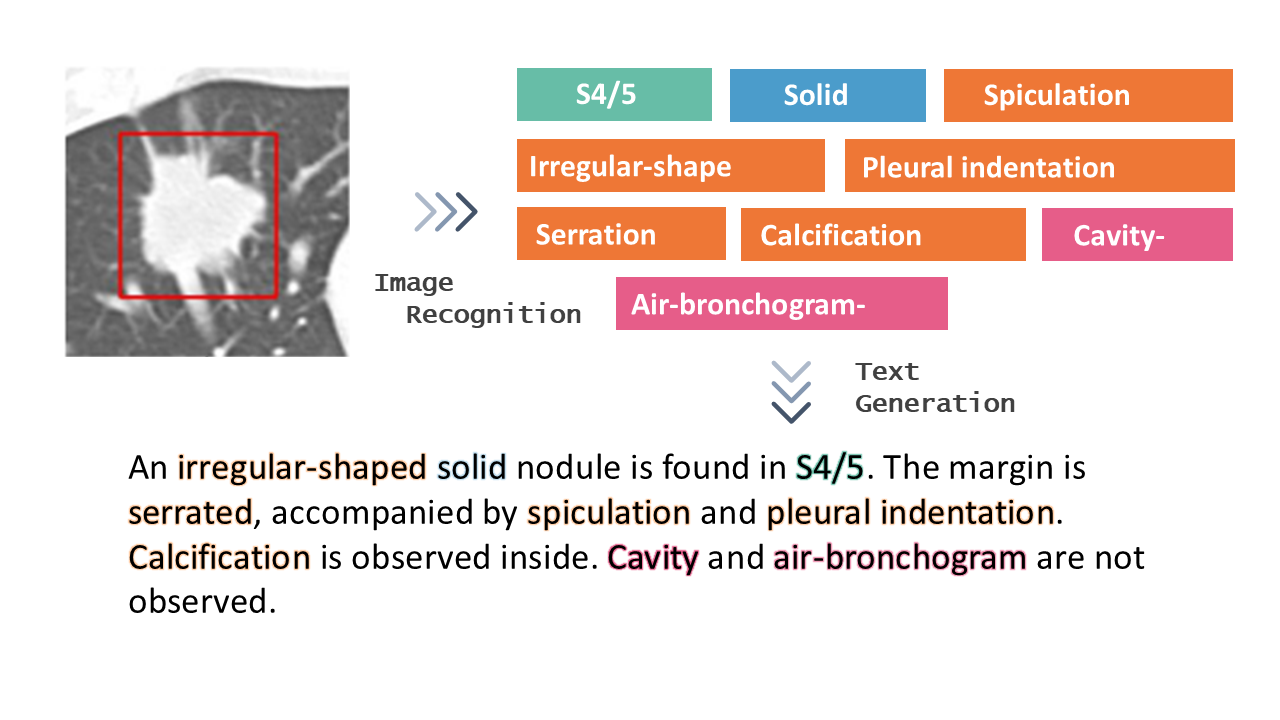
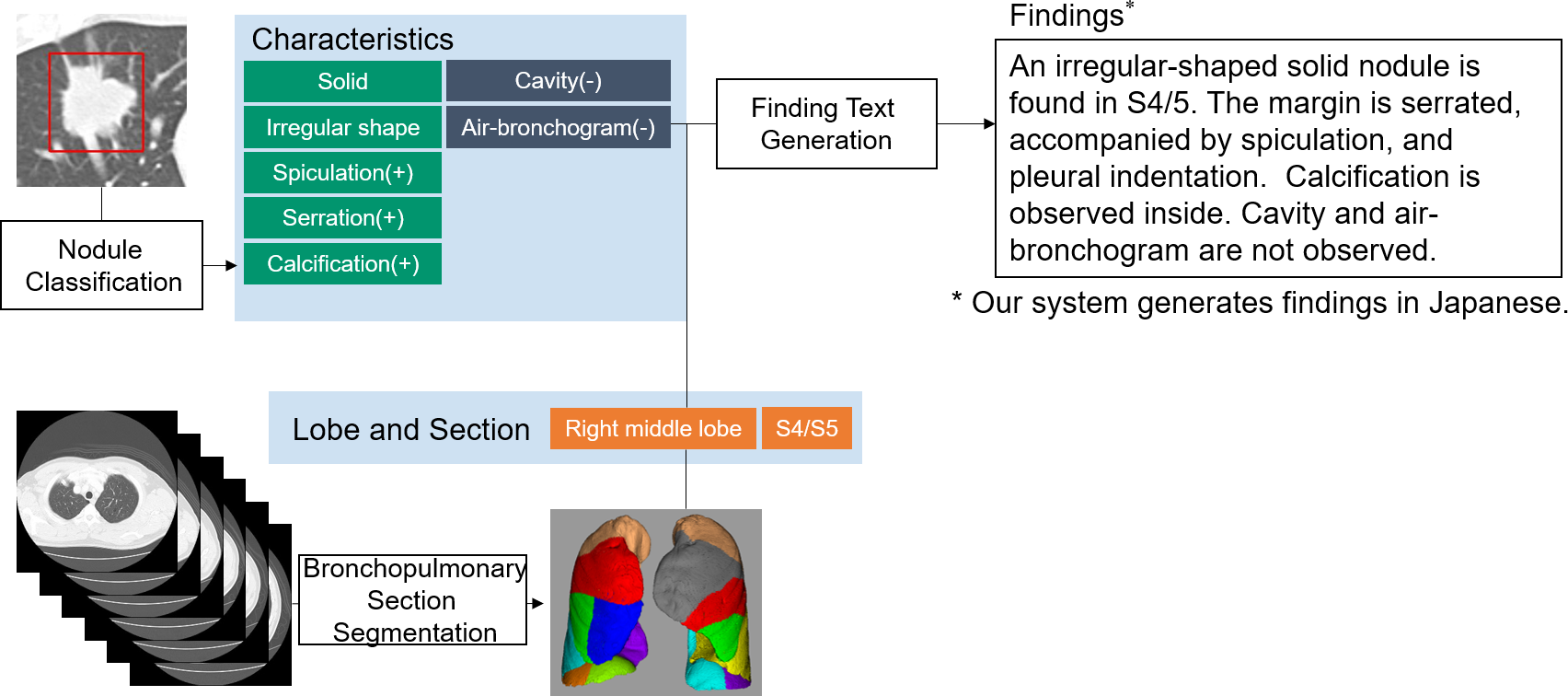
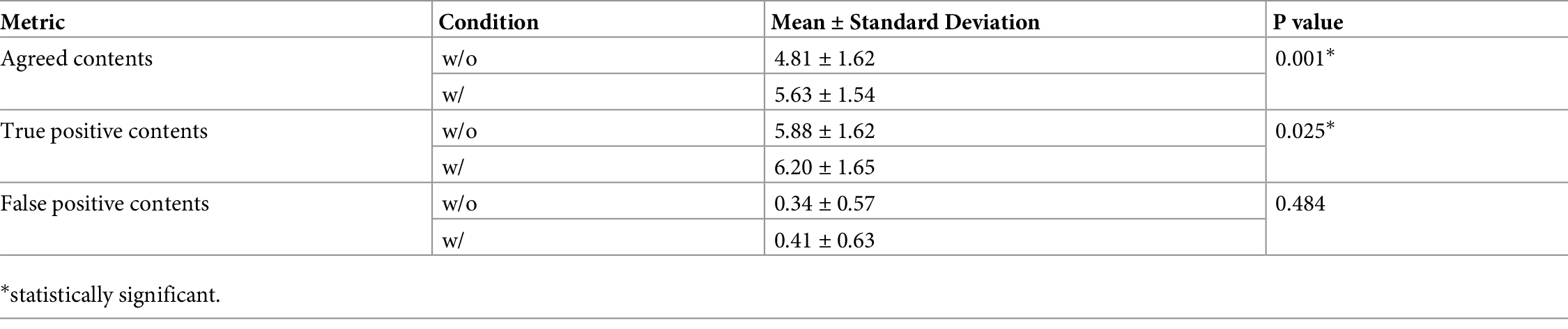
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. Computed tomography (CT) is useful to detect it. Radiologists need to record a variety of imaging findings in radiology reports. Ideally, the reports should accurately describe the anatomical location, size, and characteristics of the lesions, etc., without any variation between radiologists. However, at present, achieving this varies depending on the radiologist. In this paper [1], the authors developed a deep learning–based system that generates the descriptions of findings from lung nodules on CT images (Figure 1). The evaluation results showed that the similarity of the described findings between the two radiologists and the comprehensiveness of the contents improved (Table 1). In the future, it is hoped that this system will be applied to other organs and lesions and will assist in the creation of high-quality radiology reports.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300325
CAUTION:This is Fujifilm Global Website. Fujifilm makes no representation that products on this website are commercially available in all countries. Approved uses of products vary by country and region. Specifications and appearance of products are subject to change without notice.