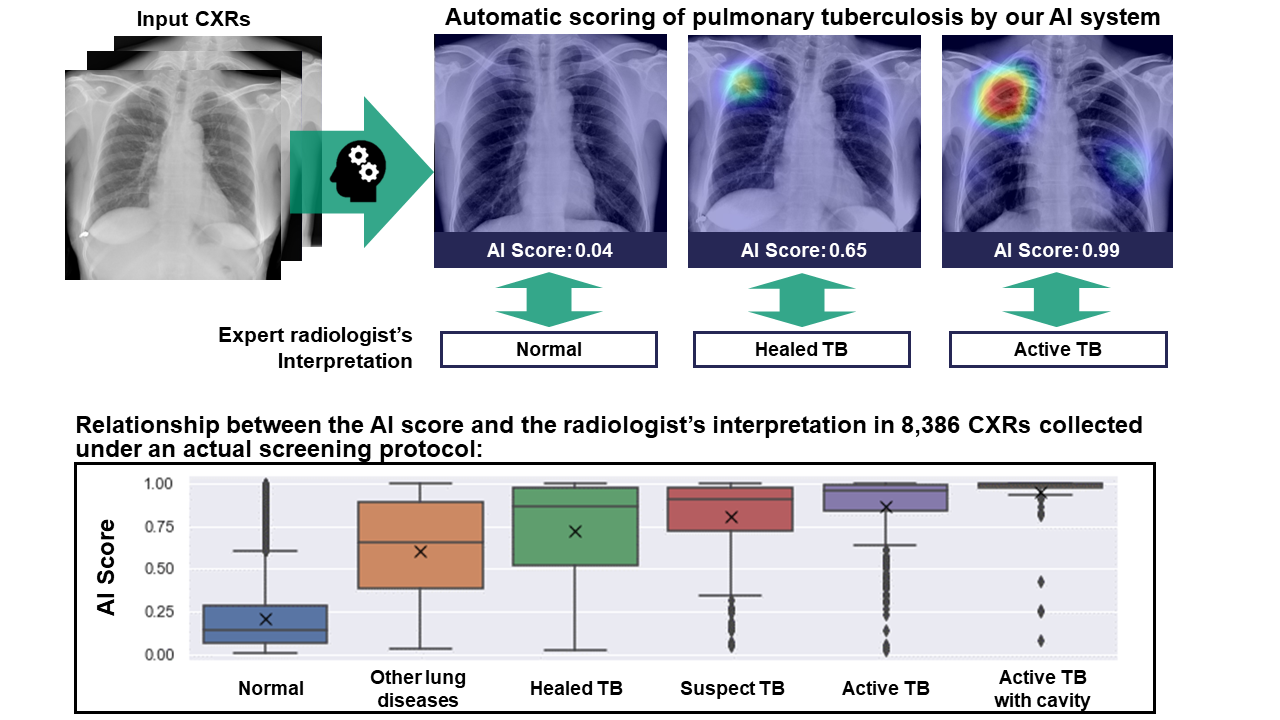
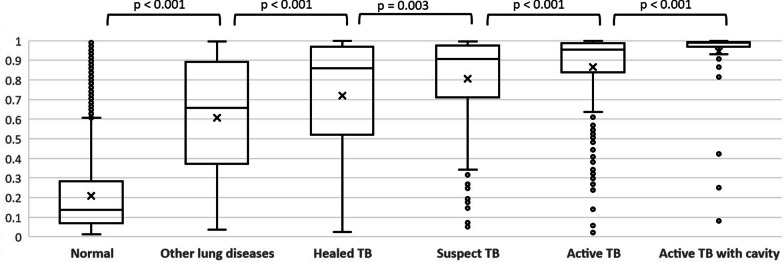
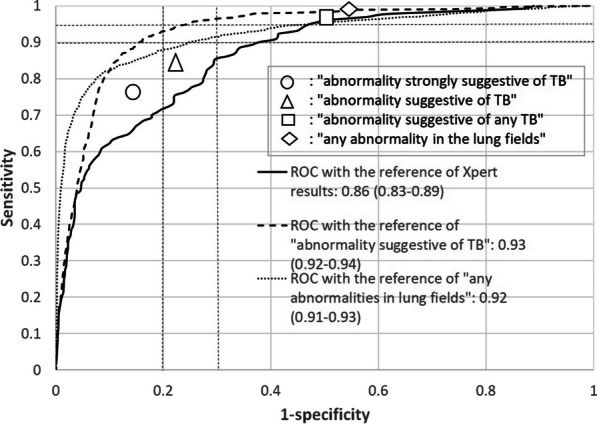
Tuberculosis (TB) is a health-threatening infectious disease caused by a bacterium, with an estimated 10.6 million incident cases and 1.6 million deaths. While the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends Xpert testing which is rapid diagnosis of pleural TB using sputum, more attention has been given to the role of chest radiography (CXR) for the diagnosis or screening because there are persons without typical TB symptoms. In this paper [1], the authors develop a new AI which predicts a classification score and a localization map of TB using a CNN (convolutional neural network) model. Performance evaluation shows that its AUROC as the bacteriological reference was 0.86 (95% confidence interval 0.83–0.89). In addition, detecting 95% of Xpert-positive TB in ACF using a threshold for triage purposes and 98% of Xpert-positive TB cases for screening purposes, respectively. In the future, it is hoped that such AI will help early detection and early treatment of TB even in areas with a shortage of expert doctors.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41182-023-00560-6
CAUTION:This is Fujifilm Global Website. Fujifilm makes no representation that products on this website are commercially available in all countries. Approved uses of products vary by country and region. Specifications and appearance of products are subject to change without notice.