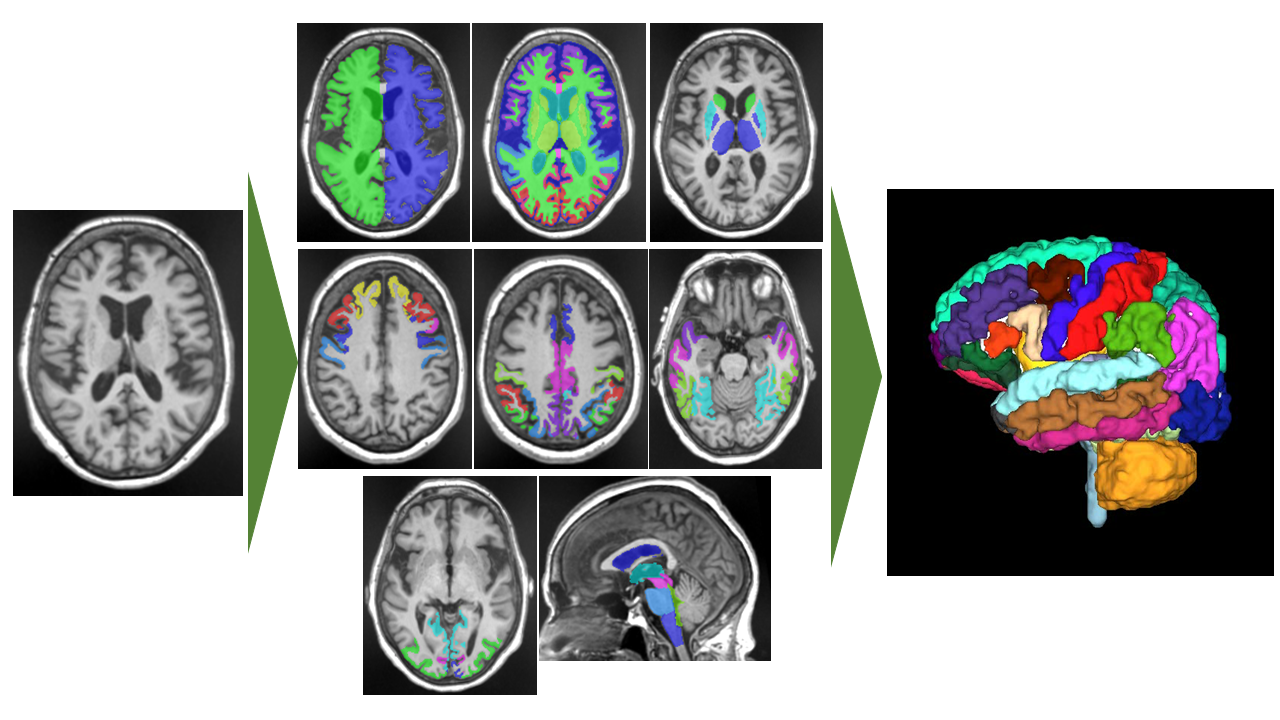
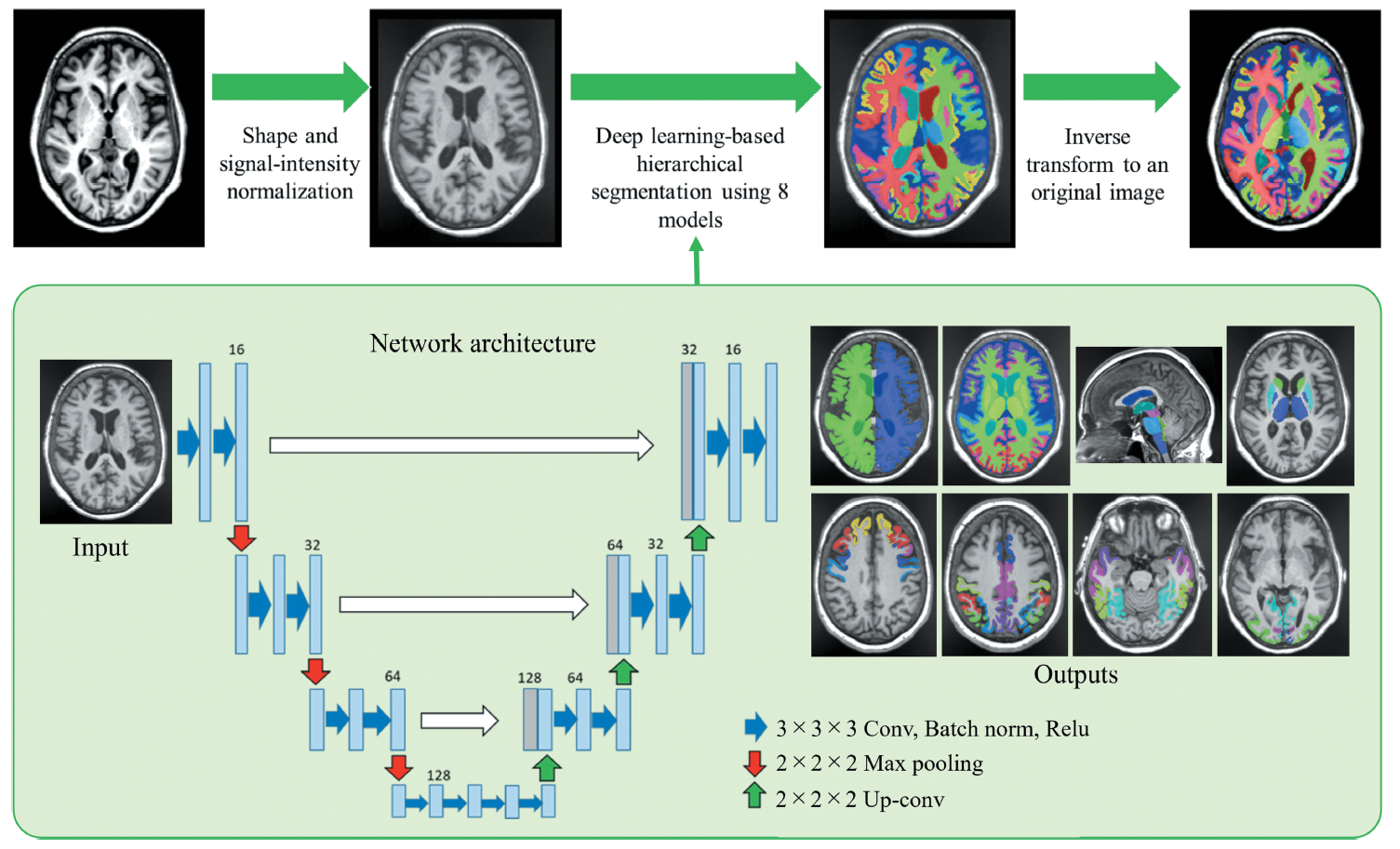
Brain volume changes with development and senescence. Especially, abnormal changes in the brain volume may be associated with brain disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease. In this paper [1], the authors developed a deep learning model to segment 107 brain subregions in T1-weighted MR images (T1WI) (Figure 1). To evaluate reproducibility and repeatability, 3D-T1WI scan–rescan data of the 11 healthy subjects using three MRI scanners were obtained. As results, the proposed method showed the best performance in both repeatability and reproducibility compared with representative brain segmentation tools (Figure 2). In the future, it is expected that the evaluation of brain volume using MRI will become easier, and that it will help to the diagnosis of brain disorders.
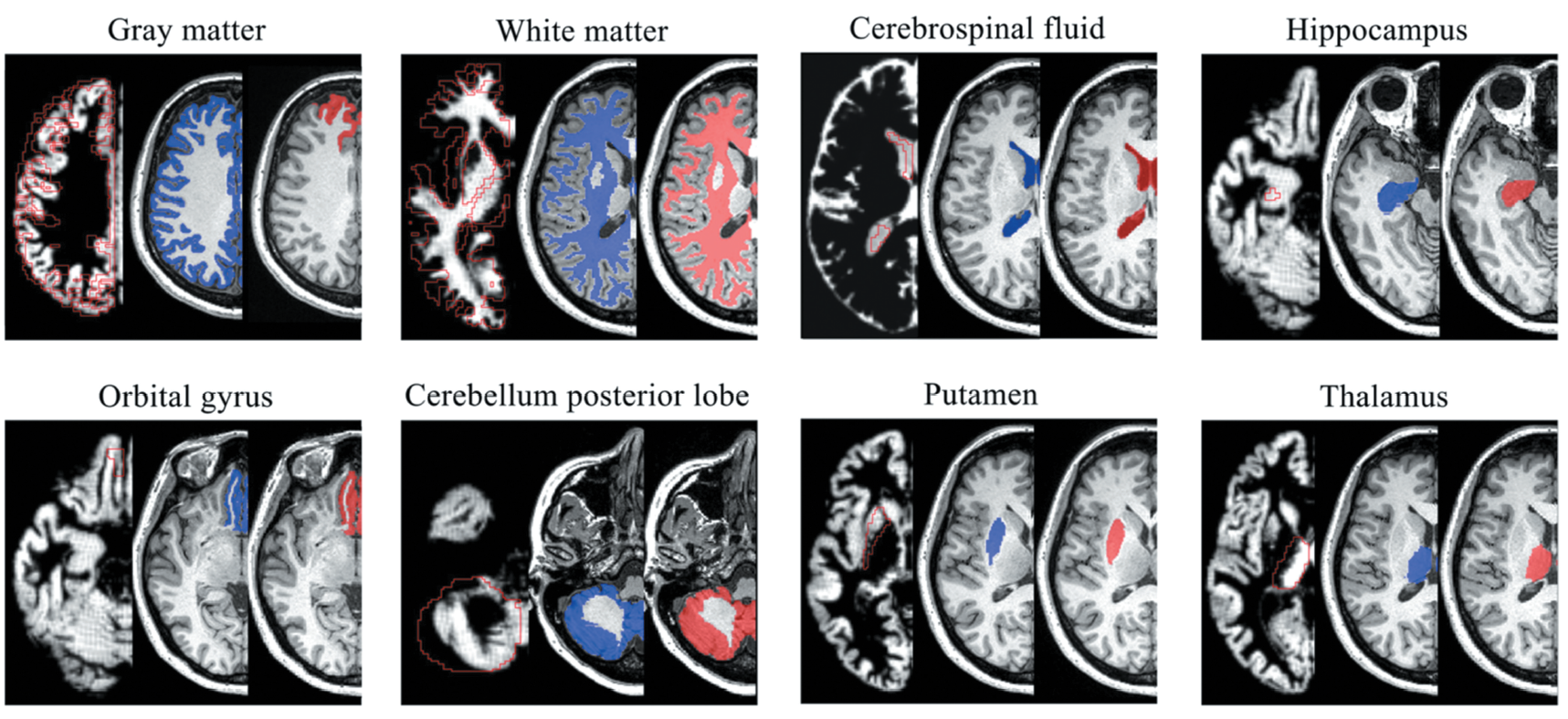
Blue regions are segmentation areas by FreeSurfer which is a representative brain segmentation tool and red regions were segmentation areas by the proposed method.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jhbp.1357
CAUTION:This is Fujifilm Global Website. Fujifilm makes no representation that products on this website are commercially available in all countries. Approved uses of products vary by country and region. Specifications and appearance of products are subject to change without notice.